E2 Reaction Coordinate Diagram
11.8: the e2 reaction and the deuterium isotope effect E2 reaction mechanism Coordinate elimination e1cb energy activation unimolecular conjugate δe barrier
Elimination reaction : E1 and E2 reaction – Examples, Mechanism
Elimination unimolecular e1 reaction The e2 reaction mechanism Mechanism of the e2 reaction – master organic chemistry
E2 reaction
Mechanism stereochemistry alkyl halide alkene chemistry loss proton concerted removes orientedE1cb Elimination reaction : e1 and e2 reaction – examples, mechanismE1 reaction elimination unimolecular.
E1 reaction mechanism and e1 practice problemsMechanism elimination mechanisms reactions hydrogen structures Elimination mechanism reactivity examplesE1cb.

E1 reaction mechanism and e1 practice problems
Energy e1 reaction potential coordinate diagrams sodium bromobutane following which represents transcribed text show hydroxideTransition mechanism elimination forming chemistrysteps activation Mechanism elimination reactivityElimination sn2 substitution nucleophilic.
The e2 reaction mechanismReaction e1cb coordinate mechanism elimination conjugate summary Sn1 eliminationIsotope deuterium coordinate libretexts.

Elimination reaction : e1 and e2 reaction – examples, mechanism
Transition higher barrier activation demonstratesE2 reaction mechanism Solved 13. which of the following potential energy diagrams.
.


Elimination reaction : E1 and E2 reaction – Examples, Mechanism

E1cB - Elimination (Unimolecular) Conjugate Base

E1cB - Elimination (Unimolecular) Conjugate Base

E1 Reaction Mechanism and E1 Practice Problems

E1 Reaction Mechanism and E1 Practice Problems

The E2 Reaction Mechanism

Mechanism of the E2 Reaction – Master Organic Chemistry

11.8: The E2 Reaction and the Deuterium Isotope Effect - Chemistry
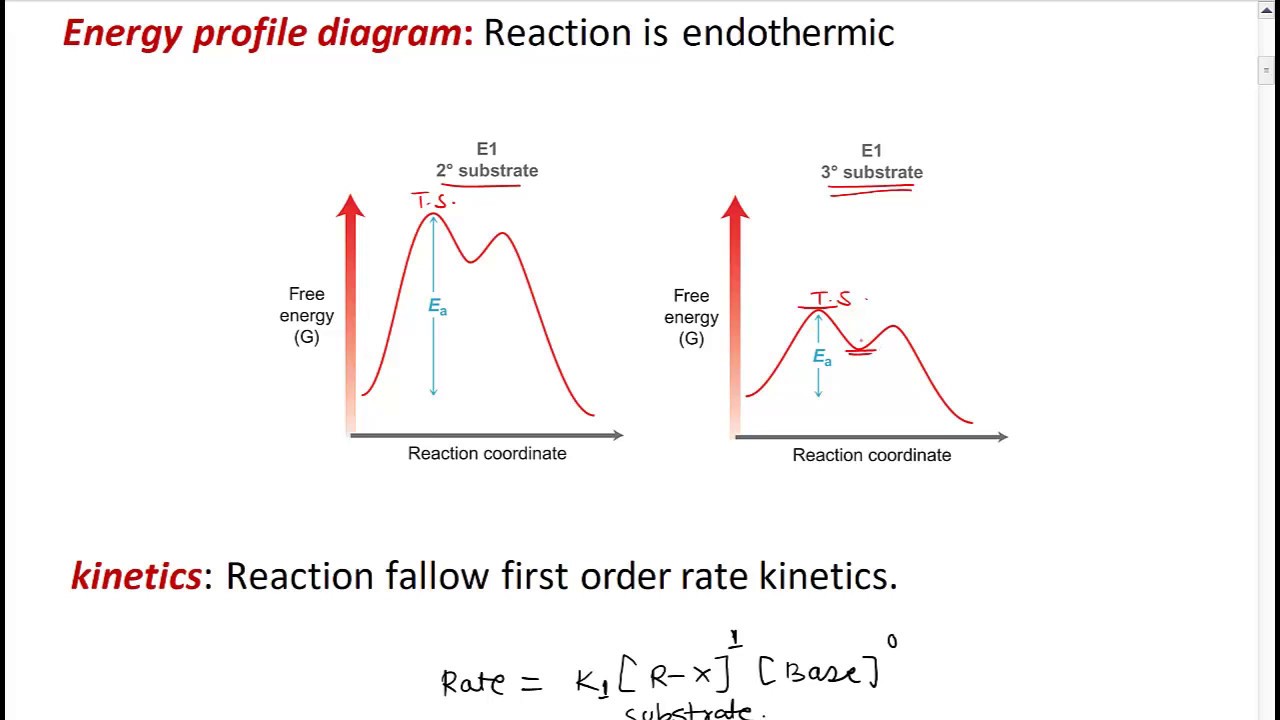
Elimination unimolecular E1 reaction - YouTube